Maintenance Tips for Raised Bed Gardens
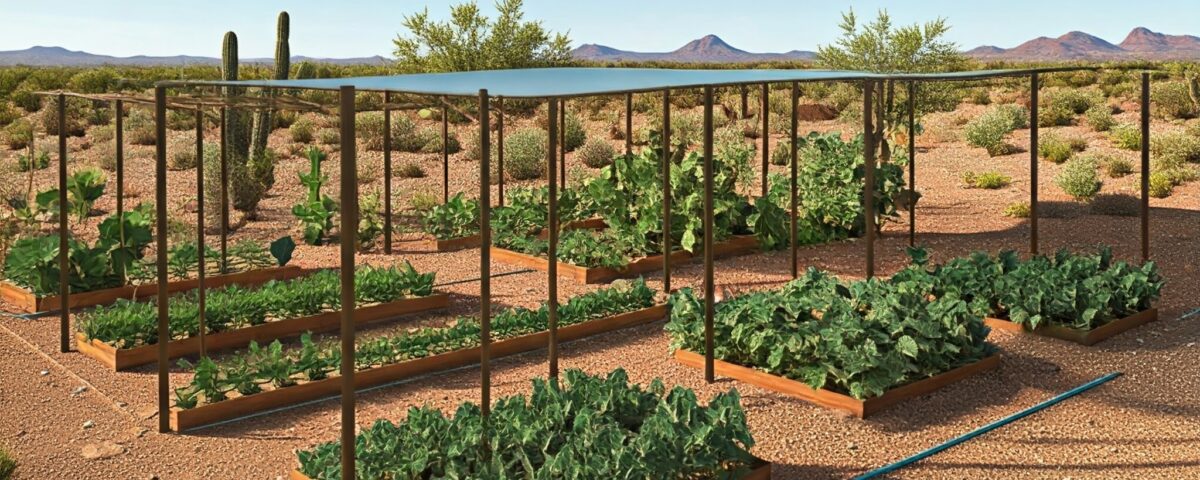

Maintenance tips for raised bed gardens are essential to keep these versatile spaces thriving, especially in the desert Southwest. Raised bed gardens are a fantastic way to grow fruits, vegetables, and herbs. They make gardening easier by improving soil quality, enhancing drainage, and creating an ornamental edible space. Regular maintenance is essential to keep your raised beds thriving. Follow this step-by-step maintenance list to ensure your garden remains productive and beautiful throughout the year.
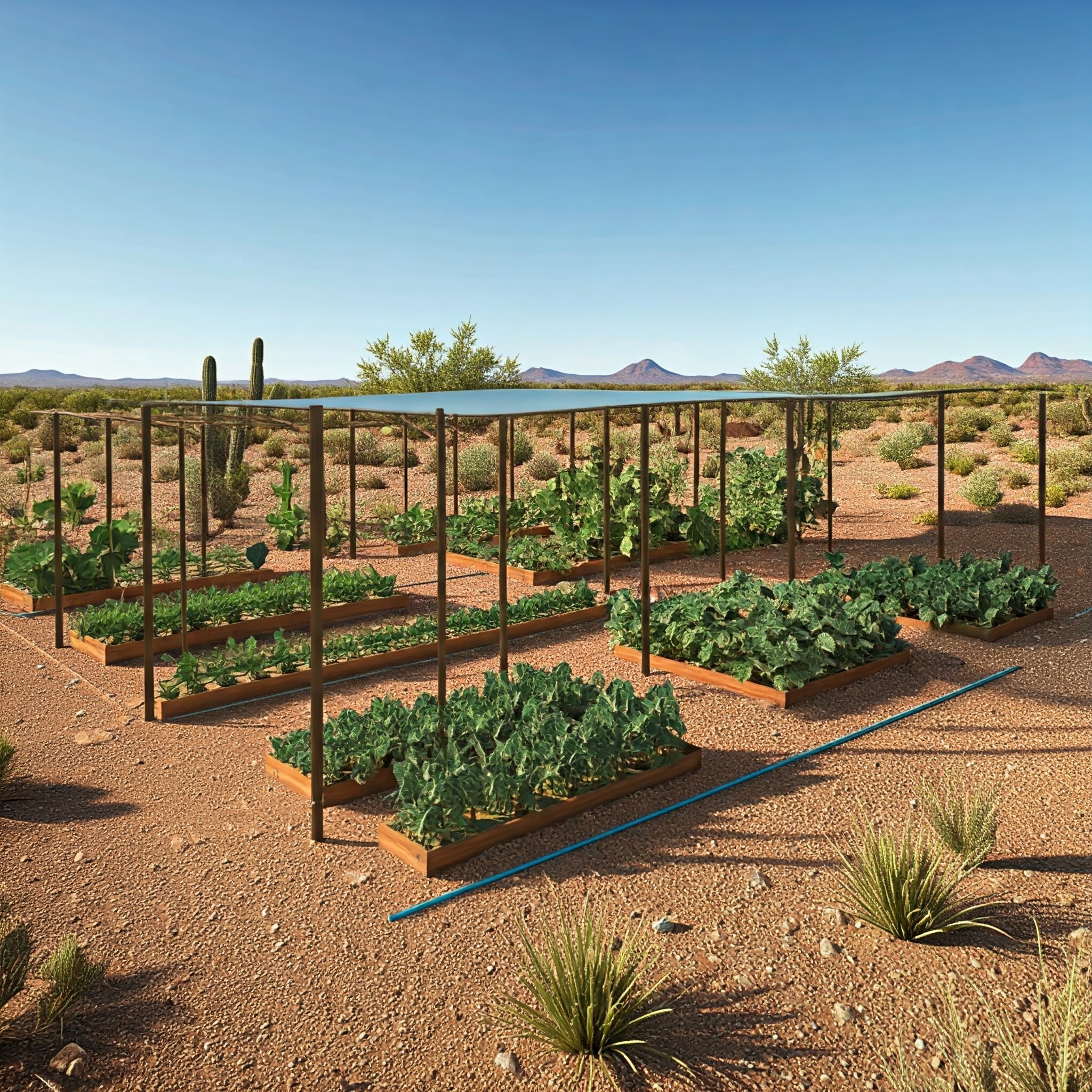

1. Water Wisely
Water management is critical for raised beds in the desert Southwest. Check soil moisture daily, especially during hot months. Water early in the morning to minimize evaporation and ensure plants get the hydration they need.
Consider using drip irrigation or soaker hoses to deliver water directly to the roots. These systems save water and reduce the risk of fungal issues caused by wet foliage.
2. Inspect for Pests
Regularly examine your plants for pests such as aphids, caterpillars, and mites. Catching infestations early can prevent widespread damage. Hand-pick pests or use organic solutions like neem oil or insecticidal soap.
Planting companion plants like marigolds or basil can also help repel harmful insects naturally.
3. Weed Regularly
Weeds are less of an issue in raised beds compared to in-ground gardens, but they can still appear. Remove weeds as soon as you spot them to prevent competition for nutrients and water.
Use mulch to suppress weed growth. Organic mulches, like straw or shredded leaves, work well while also improving soil health.
4. Check Soil Levels
Soil tends to settle over time in raised beds. Check the soil level monthly and add fresh soil or compost as needed.
A depth of 12–18 inches is ideal for most vegetables, but deeper beds may require more frequent refilling. Ensure the soil remains rich in organic matter to support healthy plant growth.
5. Fertilize Strategically
Plants in raised beds can quickly deplete nutrients, so regular fertilization is crucial. Apply an organic fertilizer once a month, adjusting it to suit your crops.
Leafy greens benefit from nitrogen-rich fertilizers, while flowering and fruiting plants need more phosphorus. Always follow package instructions to avoid over-fertilizing.
6. Inspect Raised Bed Structures
Raised bed frames made of wood, metal, or stone can weaken over time. Check for signs of rot, rust, or shifting materials.
Repair any damage promptly to prevent soil erosion and maintain the stability of your garden.
7. Rotate Crops
Avoid planting the same crops in the same spot every season. Crop rotation helps prevent pests and diseases while maintaining soil health.
Plan your garden layout with crop families in mind. For example, follow nitrogen-fixing legumes like beans with nutrient-hungry crops like tomatoes.
8. Mulch for Moisture and Temperature Control
Mulching is essential for raised beds in the desert Southwest. A 2–3 inch layer of organic mulch conserves moisture, regulates soil temperature, and reduces weed growth.
Replenish mulch as needed throughout the year, particularly before the hottest summer months.
9. Prune and Harvest Regularly
Pruning and harvesting promote plant health and productivity. Remove dead or damaged leaves to redirect energy to new growth.
Harvest fruits, vegetables, and herbs as they ripen to encourage continuous production. Leaving overripe produce can attract pests and reduce yields.
10. Prepare for Seasonal Changes
Spring
- Test your soil pH and adjust it as needed. Most crops thrive in slightly acidic to neutral soil (pH 6.0–7.5).
- Refresh your soil with compost or aged manure.
- Plan your garden layout to rotate crops effectively.
Summer
- Add extra mulch to protect the soil from the intense sun.
- Provide shade for sensitive plants with shade cloth or row covers.
- Water deeply and consistently to combat the heat.
Fall
- Clear out dead plants and debris to prevent overwintering pests.
- Plant cool-season crops like spinach, lettuce, and kale.
- Enrich the soil with organic matter to prepare for winter and build a frost cover system to protect plants (above).
Winter
- Cover empty beds with a tarp or plant cover crops to protect soil from erosion.
- Prune perennial herbs like rosemary and thyme.
- Check and maintain irrigation systems before freezing temperatures hit.
11. Troubleshoot Common Problems
If your soil is drying out, improve moisture retention by adding organic matter and applying a layer of mulch. Consistent and proper watering techniques also play a critical role in preventing this issue. For poor drainage, check for clogged drainage holes in your raised beds and ensure you’re not overwatering your plants. If pests become a problem, rotate your crops each season, plant companion species to deter harmful insects, and apply organic pest control solutions like neem oil or insecticidal soap.
12. Maintain Different Raised Bed Heights
Low Beds (6–12 inches)
- Best for shallow-rooted plants like lettuce and radishes.
- Monitor soil moisture closely as these beds dry out quickly.
Medium Beds (12–24 inches)
- Suitable for most vegetables and herbs.
- Easier to weed and maintain than lower beds.
Tall Beds (24+ inches)
- Ideal for deep-rooted plants like tomatoes and carrots.
- Accessible for gardeners with mobility challenges.
- Fill the bottom with bulky organic material to save on soil costs.
13. Focus on Sustainability
Sustainability should be at the heart of your gardening practices. Turn kitchen scraps and yard waste into nutrient-rich compost to feed your soil naturally. Choose drought-tolerant crops that thrive in the arid climate of the desert Southwest to minimize water usage. Additionally, conservation can be practiced by installing water-efficient irrigation systems and using mulch to retain soil moisture and reduce evaporation.
Conclusion
Regular maintenance ensures that your raised bed gardens remain a source of beauty and productivity. Each step contributes to a thriving garden, from managing water and pests to seasonal soil care and structural repairs. Whether your raised beds are low, medium, or tall, these tips will help you create a sustainable and ornamental edible garden that thrives in the desert Southwest. Stay proactive, and your efforts will yield a rewarding harvest season after season.

Read Our Latest Posts…
- Tips & Tricks for Planting Bare Root Fruit Trees
 Expert tips for desert gardening, from plant zoning and efficient irrigation to soil care and agriscaping for a sustainable landscape.
Expert tips for desert gardening, from plant zoning and efficient irrigation to soil care and agriscaping for a sustainable landscape. - How to Keep Your Plants Cozy and Thriving in Winter: Smart Cold-Season Gardening Techniques
 Expert tips for desert gardening, from plant zoning and efficient irrigation to soil care and agriscaping for a sustainable landscape.
Expert tips for desert gardening, from plant zoning and efficient irrigation to soil care and agriscaping for a sustainable landscape. - Seed to Supper in 7 Days: The Power of Sprouting for Fast, Fresh Nutrition
 Expert tips for desert gardening, from plant zoning and efficient irrigation to soil care and agriscaping for a sustainable landscape.
Expert tips for desert gardening, from plant zoning and efficient irrigation to soil care and agriscaping for a sustainable landscape. - Growing Abundance Anywhere: The Agriscaping Guide to Year-Round Edible Living
 Expert tips for desert gardening, from plant zoning and efficient irrigation to soil care and agriscaping for a sustainable landscape.
Expert tips for desert gardening, from plant zoning and efficient irrigation to soil care and agriscaping for a sustainable landscape. - How to Turn Waste Into Growth: The Power of Composting for a Regenerative Garden
 Expert tips for desert gardening, from plant zoning and efficient irrigation to soil care and agriscaping for a sustainable landscape.
Expert tips for desert gardening, from plant zoning and efficient irrigation to soil care and agriscaping for a sustainable landscape.
